Recent Articles Reading: Storage, Chips, Performance, Misc
31 October 2023
The Entropy part.
1. PolarDB-X 存储引擎核心技术 | Lizard 分布式事务系统
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/656922735
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/654126910
1. interesting
2. 分布式事务模型
1. Percolator模型
2. Calvin模型
3. XA模型
3. 协调日志会被下沉到存储引擎上。其中一个参与方会被选为主分支。
2. ML system 入坑指南 - Fazzie
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/608318764
1. useful materials and courses
3. 充分发挥NVMe存储的潜力:高性能存储引擎的设计与实现 - Andy730
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/pdIyXl3Z2NZ936VfVHSgjw
1. interesting. well study on NVMe SSD storage gaps and approaches
1. "我们的高性能存储引擎LeanStore专门为NVMe SSD设计"
2. Source: Gabriel Haas, Viktor Leis, What Modern NVMe Storage Can Do, And How To Exploit It: High-Performance I/O for High-Performance Storage Engines, June 2, 2023
2. Highlights
1. 解决方案是在系统的每个部分都充分采用并行性
1. 这种需求必须由高效的页面替换算法和异步脏页写入来满足
2. 由于整体的CPU预算有限,所涉及的每个组件都必须进行深度优化,并以可扩展的方式实现
3. my questions
1. "我们得到每个I/O操作的CPU预算为13,000个周期(2.5 GHz × 64核心 / 1200万IOPS)"
1. is the calculation correct?
4. Azure下一代块存储架构:深度技术解析
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/EyaDM8Oz-TqvhEkmnchdng
1. Azure Direct Drive by Greg Kramer
2. Highlights
1. DDX Protocol
2. Completion-side IO throttling
5. 主存储的未来:内存逐渐替代传统存储
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg3MDY0OTQ0NA==&mid=2247490517&idx=1&sn=d837fe65c55319487e1e8787e3eee778
1. 内存池化和内存共享是CXL联盟试图提供的重要产品
n. related materials
1. CXL 2.0 - GPU Memory Sharing and Expansion
https://www.h3platform.com/blog-detail/36
2. NVLink/Switch and Platform Wars, Micron and Datacenter
https://www.fabricatedknowledge.com/p/nvlinkswitch-and-platform-wars-micron
6. 2023年企业级存储主要发展趋势
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg3MDY0OTQ0NA==&mid=2247490328&idx=1&sn=c467bcc73b5308c43c1d4ce38ee7e6cb
1. sources
1. Source: Chris Mellor, Gartner unveils hottest storage trends for 2023, September 7, 2023
2. Gartner 《Top Trends in Enterprise Data Storage 2023》
2. Highlights
1. 存储即服务(Storage-as-a-Service)
2. 网络存储(Cyber storage)
3. QLC闪存
4. 统一文件和对象存储平台
5. 数据存储管理服务
6. 混合云文件数据服务
7. NVMe over Fabric
8. 容器原生存储
9. 专用NVMe SSD
7. 6家存储系统公司的客户反馈(最喜欢的/最不喜欢的) - Andy730
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg3MDY0OTQ0NA==&mid=2247490321&idx=1&sn=45cd7ac08aaba1100f40f74c9989d58e
1. interesting
8. Flash Memory Summit 2023 回顾
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg3MDY0OTQ0NA==&mid=2247489887&idx=1&sn=3de9eeb352719165460e25e4adf0b99a
9. GigaOm企业级Kubernetes存储雷达报告
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg3MDY0OTQ0NA==&mid=2247489871&idx=1&sn=bb5fb16fd8f66c43d6a34f43fc88af4c
1. Pure Storage
10. 5篇VAST Data的报告:思考AI基础设施的新方式
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg3MDY0OTQ0NA==&mid=2247489793&idx=1&sn=29f3c628b32e71fba1bd0b49456bf927
11. 2023年度最热门的10家数据存储初创公司
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg3MDY0OTQ0NA==&mid=2247489253&idx=1&sn=4b9996bb11ecf4d6e8fe9f69a1ae150b
1. interesting
2. Leil Storage - https://leil.io
1. "Leil Storage与Western Digital合作,利用后者的新一代主机管理式针对式磁盘(HM-SMR)硬盘和Power Disable HDD管理技术"
2. Lower power per TB by 18% with Host-Managed SMRs drives vs any other
1. interesting
2. Western Digital developed a specialised HDD product tailored for Leil Storage, integrating SMR technology and a power disable feature:
1. The power disable feature empowers Leil Storage to entirely disconnect electricity from these drives, leading to enhanced energy efficiency.
2. SMR technology facilitates a denser data storage format, ultimately lowering electricity consumption and cost per terabyte.
12. 颠覆性创新?存储界已有所耳闻 - Andy730
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg3MDY0OTQ0NA==&mid=2247489252&idx=1&sn=1b71196b274d3ee11cb7bbf3b2b2c6a4
1. VAST data - DASE architecture
1. Disaggregated Shared Everything Architecture (DASE)
https://vastdata.com/disaggregated-shared-everything-architecture-dase
2. VAST's DASE Architecture Explained
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hNkTK_SNUvQ
2. 颠覆者、持续创新者、即将推出的供应商和失败者表格
1. good table
2. Parallel Filesystem
1. 探寻文件系统的本质:技术突破与市场变革
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg3MDY0OTQ0NA==&mid=2247489241&idx=1&sn=7a2cc12f16f3823374052adff0c66ad5
1. 并行文件系统
2. 在pNFS或其它并行文件系统中,客户端的作用是拆分、条带化或分块数据
3. VAST Data Timeline 全景视图
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg3MDY0OTQ0NA==&mid=2247489206&idx=1&sn=eb73994342776e8b3a1fb3944e7ff060
1. ANDY730:
1. VAST Data 是一家堪称教科书式的成功创业公司:产品GA仅17个月后就成为最快达到独角兽估值的IT基础设施公司。
2. VAST Data 的产品/核心技术、核心团队、融资、团队建设、业务拓展/行业/客户、生态/销售渠道、市场营销、商业模式/销售/营利性等方面的战略设置和执行 - 皆显示出这是专业的上乘之作。值得我们细心学习。
4. 5篇VAST Data的报告:思考AI基础设施的新方式
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg3MDY0OTQ0NA==&mid=2247489793&idx=1&sn=29f3c628b32e71fba1bd0b49456bf927
13. 字节基于 Hudi 的批流一体存储实践
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/654263972
14. 万字长文,GPU Render Engine 详细介绍 - 字节跳动SYS Tech
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/630331896
16. Hank's View on Vector Database
https://ebjmqmuy34.feishu.cn/file/IYjAbzXgCob2iqxLACocbwjWnYd
17. 十行代码让日志存储降低80%
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/657609174
19. Transformer作者:指令型智能体的构建之法 - Aidan Gomez @ Cohere
https://www.toutiao.com/article/7255220041912730146
20. 中台反思:技术中台设计架构 - 蒋震宇
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/367039997
27. 推荐系统技术综述 - 陈祖龙 阿里巴巴 高级算法专家
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/627664537
29. 如何管理一个团队? - 成长在路上
https://www.zhihu.com/question/23094258/answer/3109455273
30. 如何应对和处置团队内部冲突? - CHO Club
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/534352428
32. AP系统中的实时更新 - Deletion in AP: COW or MOR? - 周章华
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/654928620
https://github.com/zhou317/misc/blob/main/Ap%E7%B3%BB%E7%BB%9F%E4%B8%AD%E7%9A%84%E5%AE%9E%E6%97%B6%E6%9B%B4%E6%96%B0.pdf
33. 前端用nvmf+网络用RDMA(走IB)+后端用spdk uio驱动部署ceph进行性能探究的踩坑实践 - 哈哈咩
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/650083644
34. 对话中国电子云副总裁朱国平:信创云3.0时代的机遇与挑战 - 金旺, 朱国平
https://soft.zhiding.cn/software_zone/2023/0815/3151557.shtml
35. RLHF实践 - IlikeShuhuaMilk
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/635569455
1. 大模型LLM知识整理 - Nicolas的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/641109766
36. 领域大模型-训练Trick&落地思考 - 刘聪NLP
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/648798461
37. InnoDB表压缩 - coltpython
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/551183563
38. 人脑是怎么防止梯度消失和梯度爆炸的? - 冒蓝火的加特林的回答
https://www.zhihu.com/question/380335971/answer/1537460713
39. 华为云盘古气象大模型研究成果在《Nature》正刊发表,相比传统数值预报提速一万倍以上,还有哪些亮点? - 谢凌曦的回答
https://www.zhihu.com/question/610665117/answer/3107838793
40. 首个中文版大语言模型综述来了! - AI Box专栏的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/647556858
41. Velox内存协调器(MemoryArbitrator)详解 - 红星闪闪的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/660356003
42. 简谈论文:Contention and Space Management in B-Trees - Korpse的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/618100545
43. linux 内核 spinlock 的实现 - 黄导的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/363993550
44. 怎样做行业研究? - 盐选推荐的回答
https://www.zhihu.com/question/21892952/answer/720758646
45. 股价是怎么形成的 - DONT的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/23183735
46. PostgreSQL:世界上最成功的数据库 - 冯若航的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/640480873
47. 聊聊CXL以及向量数据库未来的一点预测 - 几点 James的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/646858357
50. 流计算引擎与流数据库:从设计到场景再到未来 - Yingjun Wu @ Founder of RisingWave Labs
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/647751859
51. Dynamic Programming Strikes Back - MySQL8.0的新优化器 - 梁辰
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/369046631
62. 京东搜索EE链路演进 - DataFunTalk的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/643617948
64. NetApp StorageGRID - Object Storage for What's Next
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uO3ZnyFpo6k
65. CockRoachDB向量化执行引擎简介及Hash Join向量化实现 - 不会游泳的鱼的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/645428158
66. 万字长文,当机器人拥抱大模型 - 韩峰涛的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/630597948
15. 计算机体系结构:脉动阵列 - lawliet
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/650209037
1. interesting
2. 脉动阵列本质上也是一种流水线设计,但是其和通常意义的流水线有以下的区别:
1. 脉动阵列的PE都是一样的,这也是其称为PE的原因,因为这些模块就是一个一个的运算单元;
2. 阵列的架构可以不是线性的,可以是多维的;
3. PE的连接可以是多向的(甚至是不同的速度流动);
4. PE可以做的很复杂,可以有local memory和执行单元;
5. 此外脉动阵列也类似于SIMD运算,特别适用于对大量规则数据流进行单一计算处理的场景。但是脉动阵列和SIMD运算相比,每个PE有可能做一些不同的事情,所以脉动阵列不完全等价于SIMD。
3. 二维脉动阵列用于TPU矩阵乘法
17. Multi-Head-Attention的作用到底是什么? - MECH
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/626820422
1. good. well explained the attention model in transformer. Both easy to understand and in-depth.
18. 从 SIGMOD 23 看 RocksDB 的存算分离实践 - 黄金架构师
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/643201581
1. RocksDB on Facebook Tectonic
2. Disaggregating RocksDB: A Production Experience [2023, 0 refs, SIGMOD, Facebook]
https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/3589772
1. interesting, the stripped RS-encoded erasure coding for small sub-block appends on logging data. This is alike a typical inline EC.
2. Highlights
1. Tectonic provides many encoding schemes with different durability and availability guarantees
1. For SST files, we want highly durable encoding with low overhead as they consume the majority of the space and write bandwidth.
We chose [12,8] encoding (4 parity blocks for 8 data blocks)
2. For WAL and other log files, we need to support low tail latency for small (sub-block) appends with persistence.
We use 5-Way Replica (R5) encoding
3. For some scenarios with heavy log updates, however, 5x network overhead of R5 is too high.
Hence, on the Tectonic side, we added support for striped RS-encoded [12] small (sub-block) appends (with persistence).
1. For example, with [12, 8] encoding with 8KB stripes, we split 8 KB data into eight 1KB data buffers, generate four 1KB parity buffers and flush those twelve 1KB buffers to 12 storage nodes.
2. Inside the storage node, each 1KB buffer is appended to the XFS file corresponding to the chunk, which is usually 8MB in size.
3. Smaller stripes might be less efficient for random reads, as data needs to be assembled from multiple nodes and then decoded.
However, log files are almost always read sequentially, so this approach works well.
3. 文章的最后还介绍了一个案例:基于 RocksDB on Tectonic 的 ZippyDB。这个案例很有参考价值
1. 一个基于共识协议(e.g., Raft/Paxos) + RocksDB 实现的 share nothing 架构的数据库,如果存储放到了 DFS 上面,它的 Raft 日志放到哪里?
1. 显然,放到 DFS 上是不可能了,每次 Raft 日志持久化要刷到 DFS 上,时延太高,写入性能太差
2. 这篇文章给的 ZippyDB 的方案是:仍然保持本地三副本的模式,只不过这三个副本是位于三个计算节点操作系统内核的 shared memory 中的,不做持久化
1. 这里有一个假设,即认为多个计算节点的内核同时崩溃是非常罕见的,因此愿意承担一定数据的持久化风险
4. ZippyDB: How we built a general purpose key value store for Facebook with ZippyDB
https://engineering.fb.com/2021/08/06/core-data/zippydb/
0. Distributed key-value stores have many applications
1. μshards (micro-shards), A typical physical shard has a size of 50–100 GB. μshards is managed by a service known as Akkio
2. All transactions are serializable by default on a shard, and we don't support lower isolation levels
3. Each shard is replicated across multiple regions (for fault tolerance) using Data Shuttle, which uses either Multi-Paxos or async replication
21. 芯片制造设计、制造、封测系列全流程
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/660404155
1. 【详细】芯片设计全流程(包括每个流程需要用到的工具以及需要参与的工作人员)
https://so.csdn.net/so/search?q=%E8%8A%AF%E7%89%87%E8%AE%BE%E8%AE%A1&spm=1001.2101.3001.7020
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36045093/article/details/124659801
https://blog.csdn.net/luoganttcc/article/details/127930485
1. very good introduction
2. good introduction
22. 谈谈对OceanBase单机分布式一体化的思考 - 杨传辉,OceanBase CTO
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/641637819
1. "有一个问题,那就是每个节点用于分布式相关的 overhead 比较大,当表格和分区较多时,即使系统空转,也会消耗好几个 CPU 核用于分布式相关操作。这个问题使得 OceanBase 1.x 系列的版本只能帮助较大规模的企业解决数据库的问题,很难在中小企业做规模化复制。"
1. 可行性分析,如何消除分布式带来的overhead?
1. Good concept - 单机分布式一体化架构
1. it relates to the field that Spanner/CockroachDB/DynamoDB transaction protocols each optimized single entry read/write, to smooth distributed-single gap.
2. 原先的 NewSQL 单机性能太差,业界主流的 NewSQL 系统,比如 CockroachDB 和 YugabyteDB 的单机 sysbench 性能只有 MySQL 的 1/5 ~ 1/10
3. OceanBase 的做法是将 B+ 树数据分块的思路融入到 LSM 树存储引擎,一方面能够像 LSM 树一样具备高压缩能力,并把热点数据放在内存中提供服务,另一方面通过类似 B+ 树的数据分块思路来减少 LSM 树的写入放大
4. 迁移操作后台进行,实际运行时一般会对迁移限速。只要不是在双十一零点这样的极端场景,后台迁移都不会影响前台的在线交易请求。
5. 我认为可以进一步把全分布式的场景分为两类:
1. 一类是 OLAP 场景,OLAP 场景单个用户的数据量都很大,且维度会比较复杂,这个场景确实很难做到本地化。但是,这个场景的并发量很小,优化的关键点在于尽可能地把所有机器的资源通过并行化、向量化等手段尽可能地利用起来。
2. 另外一类是 OLTP 场景,假设某个 OLTP 业务全部都是跨用户转账操作,那么,如果数据量比较小,单机分布式一体化架构可以只部署单机,没有额外的分布式开销;如果数据量比较大,必须采用多机部署,那么,性能的扩展比虽然会大幅下降,但是,这是业务无法避免的,这种场景下单机分布式一体化数据库相比其它的 shared nothing 数据库在架构上也没有劣势。
23. 这些年在阿里学到的方法论 - 汪叽
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/642053500
https://developer.aliyun.com/article/1262780?utm_content=m_1000375490
1. 5W2H是指WHY、WHAT、WHO、WHEN、WHERE、HOW、HOW MUCH
2. STAR是一种帮助讲述故事的法则,可以让问题的描述更加清晰易懂,在面试过程中常常使用。STAR法则是情境(situation)、任务(task)、行动(action)、结果(result)的缩写。
3. 帕累托原则: 20%的人占用了80%的社会财富
长尾理论: 80%长尾可以积累成很大的份额
4. MVP - Minimum Viable Product
5. 六顶思考帽:从不同的角度思考同一个问题,每次只思考一个方面。它用六顶颜色不同的帽子作为比喻,把思维分成六个不同的方面
1. interesting
2. 白色思考帽
1. 中立、客观,关注事实和数据
3. 绿色思考帽
1. 创造力和想象力,头脑风暴,求异思维
4. 黄色思考帽
1. 乐观、正面,满怀希望,建设性
5. 黑色思考帽
1. 否定、怀疑、质疑,合乎逻辑的批判
6. 红色思考帽
1. 感性、直觉、预感、情绪
7. 蓝色思考帽
1. 冷静,负责控制和调节思维过程
2. 负责做出结论
6. 第一性原理
1. 我们运用"第一性原理"思维而不是"比较思维"去思考问题。我们在生活中总是倾向于比较--别人已经做过了或者正在做这件事情,我们就也去做。这样的结果是只能产生细小的迭代发展。"第一性原理"的思考方式是用物理学的角度看待世界的方法,也就是说一层层剥开事物的表象,看到里面的本质,然后再从本质一层层往上走。
7. SCQA
1. 情境(Situation)、冲突(Complication)、问题(Question)、答案(Answer)
2. 标准式:(SCA)情境-冲突-答案;
开门见山式:(ASC)答案-情境-冲突;
突出忧虑式(CSA)冲突-情境-答案;
突出信心式:(QSCA)疑问-情境-冲突-答案。
8. 目标管理: OKR, KPI, SMART
9. 战略分析
1. PEST: PEST是一种主要用于行业研究的分析工具,通过从政治(Politics)、经济(Economy)、社会(Society)、技术(Technology)几方面进行研究
2. SWOT分析法
1. 使用 SWOT 进行分析时,可以遵循四点原则。
1. 原则一:投入资源加强优势能力、争取机会( SO : 最大与最大策略);
2. 原则二:投入资源加强优势能力、减低威胁( ST : 最大与最小策略);
3. 原则三:投入资源改善弱势能力、争取机会( WO : 最小与最大策略);
4. 原则四:投入资源改善弱势能力、减低威胁( WT : 最小与最小策略)
10. 用户增长
1. 数仓分层
1. 构建数仓时一般可将数据分为四层,分别为原始数据层(ODS)、公共明细层(DWD)、公共汇总层(DWS)、应用数据层(ADS)
11. 海盗指标—AARRR
1. AARRR是McClure在2007年提出的,专注于获客(Acquisition)的用户增长模型,因为其爆炸性的增长方式通常又被称为海盗模型,其本质由Acquisition (获取)、 Activation (激活)、 Retention (留存)、 Revenue (收益)和 Referral (传播)5个阶段组成。
2. interesting part. more details and strategies for each stage in the article
12. RARRA模型
1. RARRA模型是托马斯·佩蒂特Thomas Petit和贾博·帕普Gabor Papp对于海盗指标-AARRR模型的优化,相比AARRR专注于获客,RARRA模型更加突出了用户留存的重要性。
2. 留存率低的情况下的获客本质是在租用流量,只有提升用户留存才能够拥有自己的用户群
13. 客户价值衡量模型—RFM
1. R——最近一次消费(Recency),F——消费频率(Frequency),M——消费金额(Monetary)
24. BytePiece:更纯粹、更高压缩率的Tokenizer - 苏剑林的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/656115828
1. 【中文分词系列】 5. 基于语言模型的无监督分词 - 苏剑林
https://kexue.fm/archives/3956
2. 为什么4090速度比A100快很多呢? - 李博杰的回答
https://www.zhihu.com/question/615946801/answer/3205148871
1. 芯片架构换血!如何评价微软在数据中心使用FPGA? - 李博杰
https://01.me/2017/01/microsoft-fpga/
25. 如何在工业界优化点击率预估:(一)开篇 - 小潄的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/462090167
样本:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/465670474
特征:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/485960208
兴趣|序列建模:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/22479936
特征交叉建模:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/489284765
多场景建模:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/489284765
图建模和预训练:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/491323844
Debias&Loss&校准:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/486798320
集成学习&模型压缩:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/488441375
0. very good series. experiences and insight summarized by team leader / architector level
1. 你真的懂点击率(CTR)建模吗? - 朱小强
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/372048174?utm_psn=1698783199348613120
26. 计算机网络的新黄金时代(一):数据中心网络 - 李博杰
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/647936483
广域网: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/650083644
无线网络: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/647939288
1. 网络和系统领域创新的两大驱动力是应用需求和硬件能力
27. 云计算服务器技术市场分析 - AWS、Azure、阿里云、腾讯云、华为云深 - 吴建明wujianming
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/645935268
1. interesting
31. 网络的智能应该放在哪里:网卡、交换机还是 xPU - 李博杰
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/657498193
1. Trend 1: intelligent devices: SmartNIC, FPGA, ASIC, NP, DPU
Trend 2: fast interconnect: NVLink, CXL
Convergence on AI and Cloud networking
46. 数据库碎碎念 - leiysky的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/645811161
1. interesting
2. how Oracle went successful
3. the success points of Snowflake
4. the future of database
48. 我组建FinOps团队的一些经验 - 张伟
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/jdBK1YDGCZDjibA0LzqbGw
1. interesting. cloud ops with a focus on cost management
49. AWS 数据底座 S3,万亿数据规模下是如何做到数据"强一致性"的 - WuKongCoder
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/658146484
1. 2020年12月份之前 AWS S3 只支持最终一致性
1. Now strong consistency: 收到成功的 PUT 响应后发起的任何读取(GET 或 LIST 请求)都将返回 PUT 请求写入的数据
2. Diving Deep on S3 Consistency - Werner Vogels
https://www.allthingsdistributed.com/2021/04/s3-strong-consistency.html
2. "我们在持久层中引入了新的复制逻辑,该逻辑充当我们的至少一次事件通知传递系统和复制时间控制功能的构建块。这种新的复制逻辑使我们能够推断 S3 中每个对象的"操作顺序"。这是我们的缓存一致性协议的核心部分"
50. 分布式块存储之调优方法论-1 综述 - 哈哈咩
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/645673037
方法论 - 理论模型 && 硬件排查 part 1:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/647079522
方法论 - 硬件排查 part 2:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/648728401
1. 性能调优整体目标
1. "由于全闪+nvmf协议对磁盘性能带来的巨大提升,现代存储系统基本上都采取轮询的模式下IO,因为一个IO发下去之后几乎能够很快返回。
因此现代分布式存储系统性能在软件无问题和其他硬件资源充足的理想条件下主要的限制基本卡在网络上(这个后面有空了单独会拿出来讨论),
我们的调优目标理论上就是如何尽可能的打满网络带宽。"
2. interesting
51. ByteFUSE分布式文件系统的演进与落地 - 字节跳动SYS Tech
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/647800478
1. interesting. many optimizations to be borrowed
52. 精读论文:ScaleStore: A Fast and Cost-Efficient Storage Engine using DRAM, NVMe, and RDMA. - Korpse的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/613398904
1. same author Viktor Leis with LeanStore. interesting work
2. 使用多台机器来支持 Larger-than-memory。NVMe-SSD的延迟比内存慢了两个数量级,但是 RDMA(远程直接内存访问)的延迟比 SSD 小一个数量级,也就是说从其它机器的内存上拿数据比从磁盘上直接拿数据要快很多。
3. 分布式缓存的一致性控制协议(page coherence protocol)
1. 由于每个 page 可能会分布在不同的节点上,StoreScale 需要设计一种方法来确保不同节点上的 page 的一致性,这里和缓存一致性协议 MESI 的功能是比较相似的。
4. 高效的 eviction 策略(page eviction)
1. Epoch-Based LRU
2. 一个独立的 evict 线程:抽样部分 page 来判断 page_epoch 的分布, 并根据需求(10%)淘汰所有epoch比较小的 page。
53. 基于Rhino的新工作:一种适应网络不稳定的流水线调度技术 - 刁岚松的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/611625055
1. "网络条件好的时候,FIFO维持数据高位;网络条件差的时候,FIFO维持数据低位。由FIFO供数的下游功能单元大部分时候不用等数据。这就是这个工作的出发点。"
54. 如何提高cache的性能? - 张若谷的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/639726264
1. good summary and ending table. Well written. CPU cache design.
A summary of many optimization patterns, in well details and easy to read.
Many aspects in hardware design that can also be borrowed.
2. highlights
1. victim cache
1. set associative cache 为内存分配一组资源 - cache entry set。但程序对资源的使用是偏斜的,很可能某一组set溢出。引入 victim cache,作为所有set共享的一个溢出扣减,相当于增大了所有 set 的大小。
2. my questions
1. 同理可以推广到任何资源分配场景,例如CPU的L1、L2、L3 cache作为上级的共享溢出
2. 这个模式也类似与池化,
3. articles in the same series
1. 为什么要有Cache? - 张若谷
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/636215219
1. Useful. Well written.
2. 如何设计Cache? - 张若谷
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/637854431
1. Useful. Well written.
m. other materials
1. 众多的AI加速架构,它们都有什么区别? - 周永权的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/450942767
1. very good article
2. 芯片架构分类
1. GPGPU类,以SIMD为基础和核心,为AI拓展了较小的Tensor core(几百OPS/Cycle),整个芯片几十到百来个SM/CU,硬件调度Grid/Block。以Nvidia Ampere,AMD MI200为代表,包括包括国内几家以AI训练和推理为方向的初创公司架构,也可以包括寒武纪MLU架构。
2. 以AI计算中GEMM/Conv为目标,围绕较大的MAC阵列设计的架构,MAC通常在边长256*256/128*128/64*64的范围,希望通过大阵列提供高能效。前期主打的是推理,后面也可以拓展到训练。以Google TPU为代表的新的AI架构,包括海思达芬奇,特斯拉FSD的NPU核等。
3. 以DNN网络计算特点为基础,众多小核组成网格布局,软件栈编译器切割调度模型为主,希望通过最好的调度减少数据流动的能耗。小核用比如RISC-V,没有MAC阵列或者很小,以Graphcore IPU和Tenstorrent的Tensix core为代表,还有Cerebras的盘子一样大的Wafer Scale Engine 2。
4. 某一些专用领域的推理NPU,比如OPPO的MariSilicon X,还有一些SOC里专用给ISV/CV功能的NPU核心。这些核心对应相关需求定制化,包括精度,量化,pipeline设计等,以达到更高的能效。
5. 以数据流为设计中心的架构,张量流处理器,代表是Groq的TSP。
6. 基于光学矩阵计算单元的数字/光学混合架构,类似第2类架构,对应的有较大(128*128/64*64)的光学矩阵,以Lightintelligence和Lightmatter为代表。
7. 存内AI计算/存算一体芯片,国内外都有不少公司已有相关芯片,包括达摩院也发布了一款。
3. 总结一些架构思考角度,非常精简
1. 指令集,其实是一个芯片架构的综合体现,也是其中的一个精髓;
2. 核内(SM/CU/AI core)架构的分析和推断
1. Tensor core/Matrix core/MAC,AI计算的核心:Conv/GEMM加速;
2. Vector core,DNN中还有很大一部分的Vector操作,它们对能效的影响;
3. 核内存储系统(Buffer 和/或 L0/L1 Cache,Register)
4. 核内pipe间并行和调度:ALU(Matrix/Vector/Special Function),Memory(Load/Store from buffer or DRAM);
5. 核内调度的粒度和实现:thread/warp/CTA级别的
3. 核间架构的分析和推断
1. 单算子tiling(Grid/Block)并行工作流程,软件还是硬件调度,思考可能的实现方法;
2. Fused op的可能性,实现方法,难以程度和收益;
3. 全模型的工作模式,软硬件的协同:包括硬件(MCU),编译器,软件栈的协同;
4. 控制command的工作方式和,同步,等等
4. 能效比分析
1. 性能,功耗,只从架构角度,包括静态的TOPS/W,以及核心利用率的考量,端到端的推理训练性能/W。
5. 通用性分析,覆盖的算子,支持新算子的难易程度。
6. 编程模型和编程接口,编译器难度,如何对接训练框架等。
7. 产品的业务落地所需要的特性支持。
2. 一些关于芯片设计的想法 - Wei Hu的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/386376370
1. Good
2. 存储、互联和计算如何设计和匹配
3. 2D计算 vs 1D 冯诺依曼计算
3. 芯片军备竞赛新十年 - mackler的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/654968895
1. Good. Visions over software hardware co-evolution
4. 处理器与AI芯片-Google-TPU - eyesighting的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/646793355
55. Have we reached consensus on consensus? - TiDB 谭新宇
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/581125699
1. useful slides to explain Multi Paxos and Raft
56. He3DB 架构设计思考 - He3DB-移动云
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/561946532
1. He3DB是受Aurora论文启发,移动云研发的云原生数据库
57. 颠覆性的分布式存储系统 -- Vast Data - hongsong wu
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/663674536
https://vastdata.com/whitepaper/#V-TreesforFastAccess
1. very good. many aspects to dive in.
2. highlights
0. A summary of key features
1. Disaggregated everything, DASE
2. QLC flash, NVMoF, Infiniband NIC
3. SCM write buffer
1. A 2U server ships 9.6TB SCM and 664TB flash
4. Similarity Reduction besides compression, dedup,
5. Wide stripe EC less than 1.1x overhead
6. With Large Data Stripes, Drives Never Need to Garbage Collect
7. Serve object storage with database
8. Geo-distributed and unified with cloud
1. DASE
1. Disaggregate everything. When expanding storage scale, no need to buy memory or compute altogether. Controllers are stateless.
2. 命名空间粒度的极端级别:文件级、对象级、表级
3. A unified DataStore, DataSpace, DataBase
1. VAST DataStore is the base
1. and serve object storage, NFS/SMB filesystems, VM volumes
2. DataBase for tables, and object metadata
3. DataEngine for lambda functions
4. DataSpace for geo-distribution and cloud
2. DataStore
1. SCM写入缓冲区在落盘SSD前吸收用户写
2. A Breakthrough Approach to Data Protection
1. Wide Stripes for Storage Efficiency
2. VAST Data Locally Decodable Codes
3. A 2U server ships 9.6TB SCM and 664TB flash - good part
1. Below is the 2U DBox node. 1U DBox node is ~1/x storage capacity.
https://support.vastdata.com/hc/en-us/articles/8900829606044-DBOX-2U-2-Node-NVMe-Enclosure
3. "借助大数据条带,驱动器无需进行垃圾收集" - good part
1. "数据按照写入 I/O 的大小写入 SCM 写入缓冲区,以最大限度地减少延迟
它被自适应地分成可变大小的块(平均大小 16-64KB)并减少
这些数据块被紧密打包成纠删码,每个数据块都是页面大小的倍数,因此 SSD 控制器可以写入整页
每个纠删码条带由许多子条带组成,创建的纠删码条带大小是 SSD 擦除块大小的数倍"
2. "VAST DataStore 以 1 MB I/O 写入 SSD,这是底层闪存 64 KB-128 KB 页面大小的显着倍数 ..
将 1 MB I/O 分层到每个 SSD 上更大的 1 GB 数据条中 ..
当VAST DataStore执行垃圾收集时,它会从每个SSD中擦除整个1 GB擦除代码带 ..
1 GB 条带深度和 1 MB 子条带深度在 VAST DataStore 架构中并不是根本上的固定值"
3. "Foresight 根据数据的预期寿命将数据写入擦除代码条带,从而最大限度地减少由垃圾收集产生的写入放大。"
4. "With Large Data Stripes, Drives Never Need to Garbage Collect"
1. System level garbage collection is still there
2. "Pre-existing data will remain in the SSDs it was originally written to and will, over time, be progressively restriped when the system performs routine garbage collection. VAST Systems don’t aggressively re-balance data at rest on the senior enclosures because that would cause write-amplification and impact performance without any real benefit. Data on the existing enclosures is already wide striped across at least 44, and most commonly 100s of SSDs there’s limited advantage to striping data even wider."
4. "VAST 集群在该池中执行磨损均衡"
1. "VAST 数据存储还通过将集群中的 PB 级闪存视为可由任何 VAST 服务器进行全局管理的单个擦除块池来扩展闪存耐用性。"
5. "突破性的数据缩减方法"
1. "VAST DataStore 使用了这两种技术" - 压缩, 重复数据删除
2. "并且还添加了一种称为相似度降低的新技术。
这减少了存储与现有块相似但不相同的数据块所需的存储量" - good part
1. Similarity Reduction
1. All Data Reduction Is Not Created Equal
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6qbc7R0W1d4
2. Similarity hash to cluster data into groups, then delta compress based on the reference cluster. Applicable to data science that data are similar but with variance, and backup. Operation granularity (bytes) can be much smaller than dedup (KBs).
3. ZSTD dictionary is also used
7. VAST Database
1. columnar, allow update, support transaction
1. support both OLTP+OLAP
2. Read benefits from scanning small column blocks (32KB). skipping by min-max filter.
1. looks like it's not building index per column
2. Virtual Parquet to supply data for interoperability
8. VAST DataSpace - Global data distribution
2. strong consistency implemented with exclusive write lease. Read always gets the latest value.
9. VAST DataEngine
1. Circumventing Data Gravity
1. interesting concepts
10. others
1. Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/VAST_Data
2. Gartner DFS & ObjectStorage: https://www.gartner.com/doc/reprints?id=1-2BG8L8TW&ct=221019&st=sb
58. NetApp StorageGRID - Object Storage for What's Next
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uO3ZnyFpo6k&t=2031s
1. Geo-distributed erasure coding. Layered. Interesting
59. Building and Operating a Pretty Big Storage System (My Adventures in Amazon S3) | USENIX by Andy Warfield
https://www.usenix.org/conference/fast23/presentation/warfield
1. Very good. Many pickups from AWS S3 experience and worth drilling down.
2. highlights
1. S3 is 17 years old
2. Per selling cloud to customers, the customers are also mostly engineers. The conversation is usually engineer to engineer that can go into quite depth.
1. This seems different from traditional commercial storage, which is typically sales to procurement.
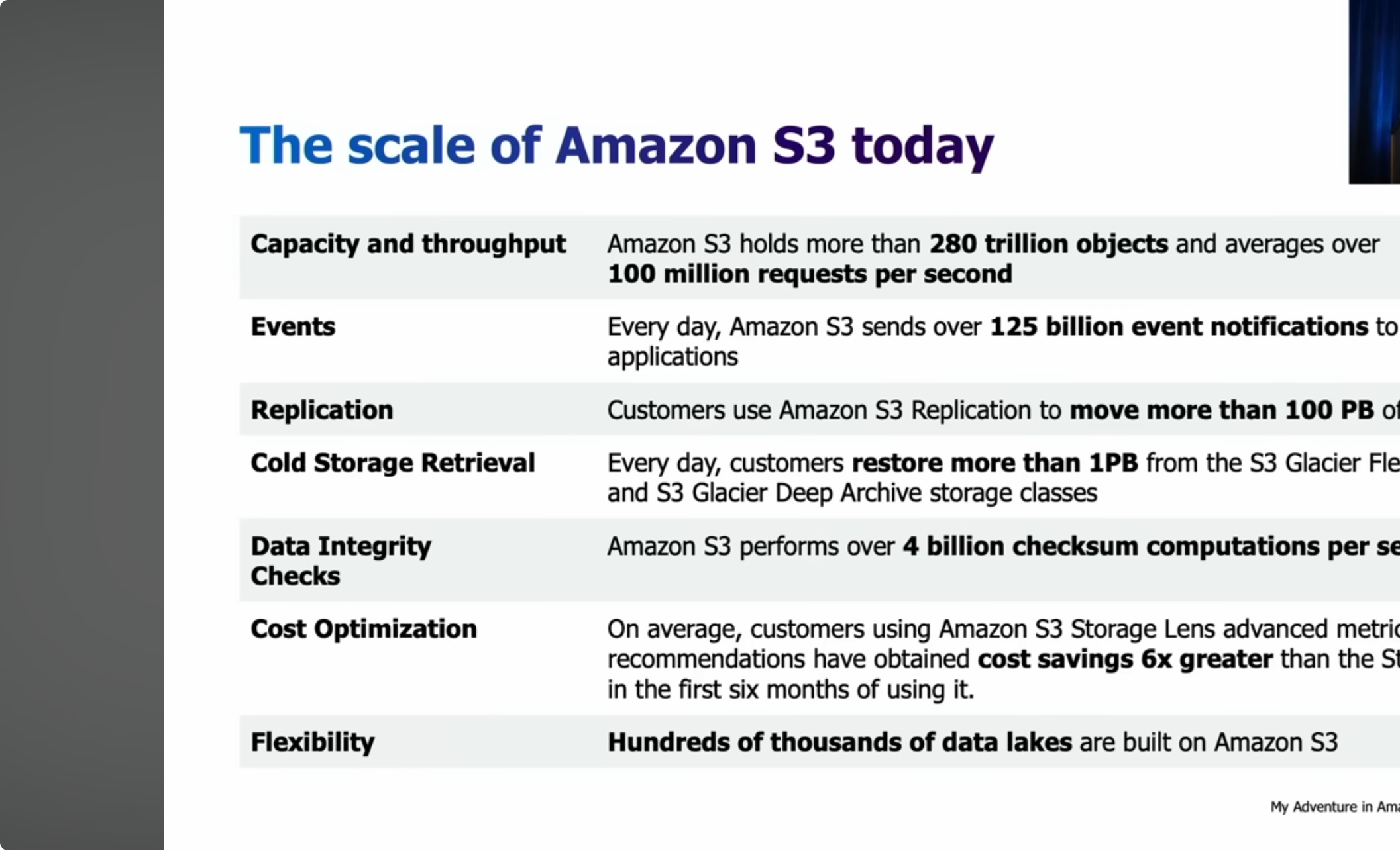
3. The scale of AWS S3 toady. Good to use as a reference.
1.
4. AWS S3 event notification.
https://medium.com/avmconsulting-blog/amazon-s3-event-notifications-321a2065b3eb
1. At-least-once, filter rules
2. messaging queues, storage functions / lambda
5. Disk evolving history and speed
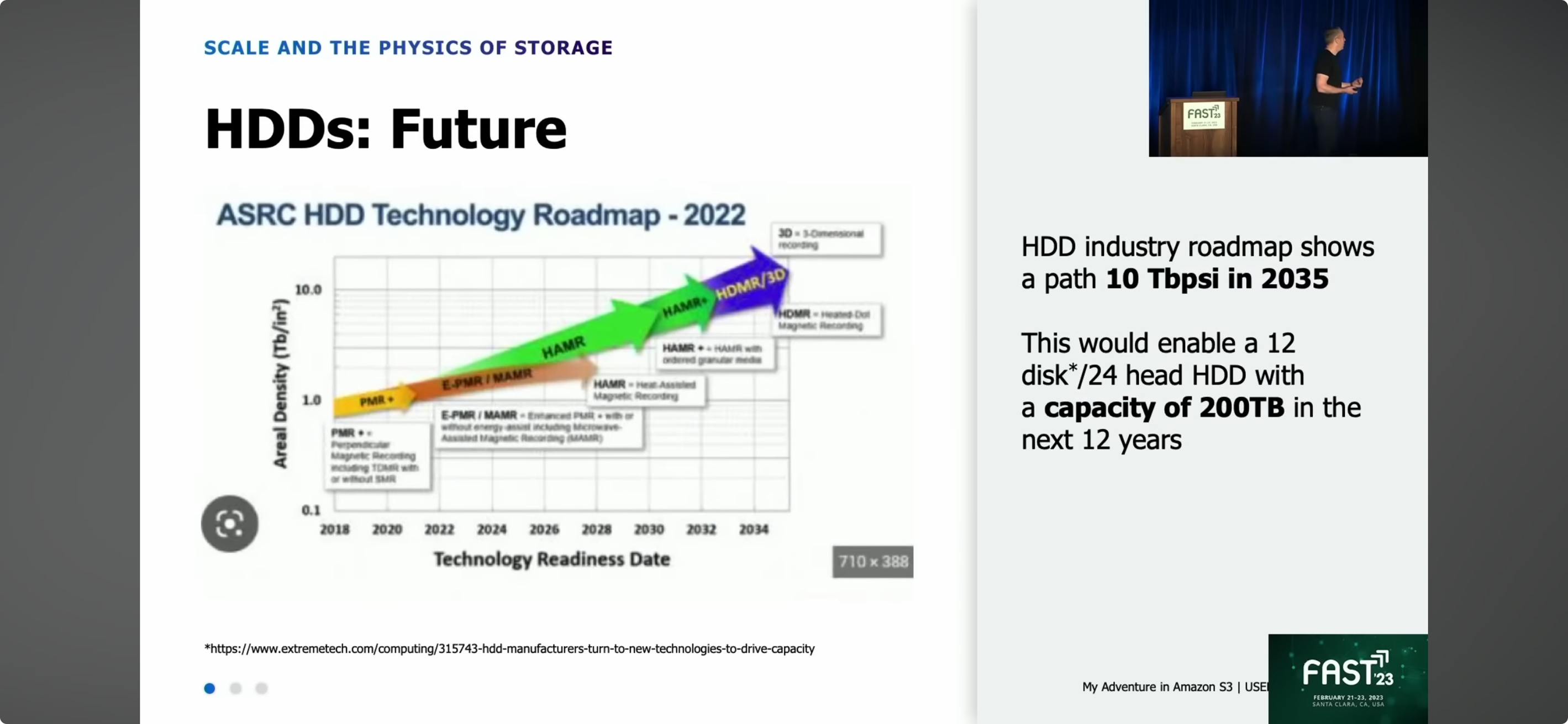
1. A new Advanced Storage Research Consortium HDD Technology Roadmap
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9918580
2. HDD Manufacturers Turn to New Technologies to Drive Capacity
https://www.extremetech.com/computing/315743-hdd-manufacturers-turn-to-new-technologies-to-drive-capacity
1. "Companies like Toshiba, Seagate, and Western Digital have shown off their next-generation technologies like Energy-Assisted Magnetic Recording (EAMR, WD) and Microwave-Assisted Magnetic Recording (HAMR, Seagate), but both companies seem to be having trouble shipping drives in significant quantities."
3. By 2035, we will have 200TB HDD with 12 plates 24 heads. (MAMR, HAMR)
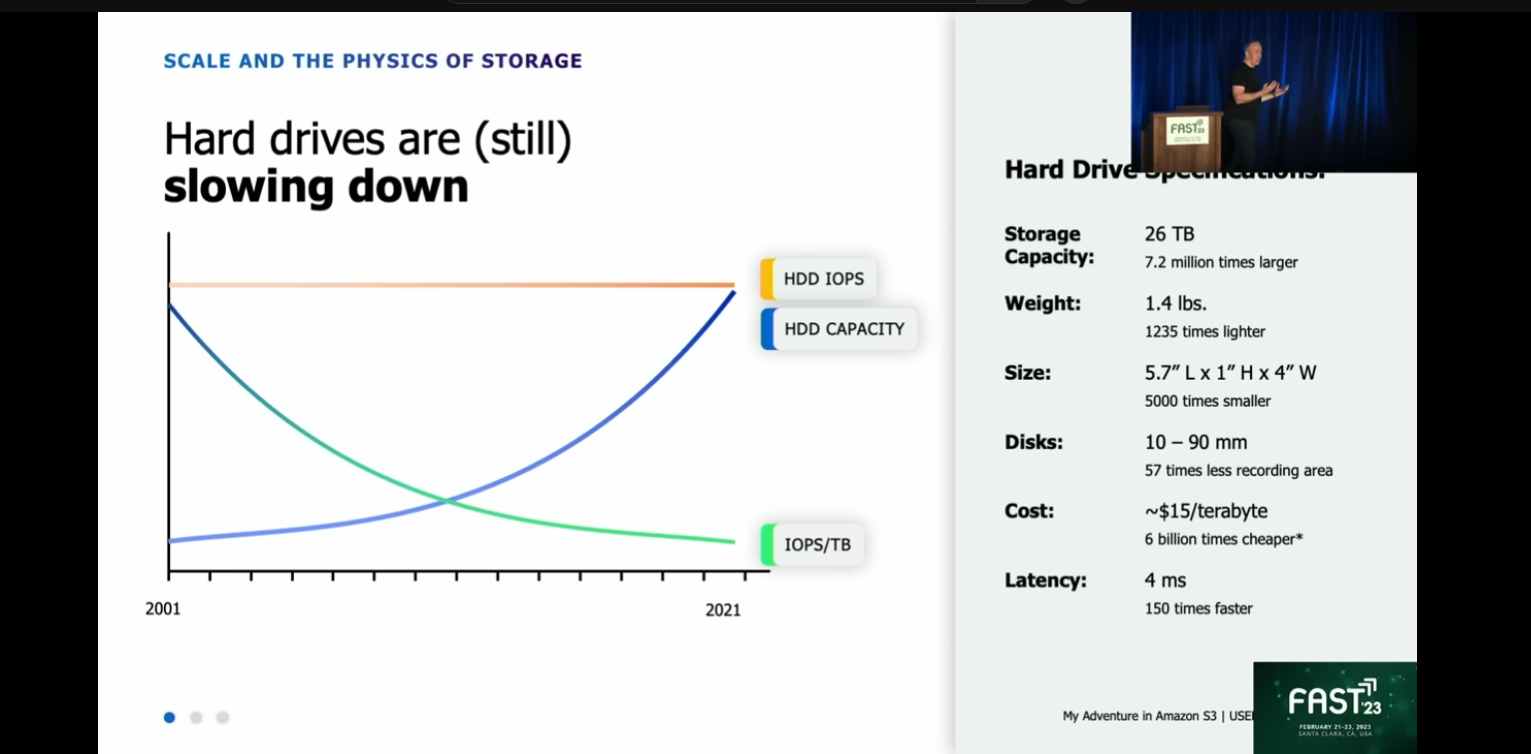
4. HDD is still slowing down
1. Cost ~$15/TB, latency ~4ms.
2. The seek time was almost the same with 17 years ago when AWS S3 launched.
5. Western Digital Ultrastar DC HC670 HDD - 26TB size
https://www.westerndigital.com/products/internal-drives/data-center-drives/ultrastar-dc-hc670-hdd?sku=ultrastar-dc-hc670-26-tb
1. "26TB1 is achieved by combining Western Digital’s OptiNAND™ technology with UltraSMR, energy-assist magnetic recording (EAMR), a 2nd generation triple-stage actuator (TSA), and proven HelioSeal® technology."
1. This is an SMR drive.
1. "Industry-first EAMR and TSA technologies with HelioSeal and host-managed UltraSMR"
2. Tech Brief - UltraSMR
https://www.westerndigital.com/products/internal-drives/data-center-drives/ultrastar-dc-hc670-hdd?sku=ultrastar-dc-hc670-26-tb
3. White Paper - Shingled Magnetic Recording
https://documents.westerndigital.com/content/dam/doc-library/en_us/assets/public/western-digital/collateral/white-paper/white-paper-shingled-magnetic-recording-hdd-technology.pdf
4. Full specification
https://documents.westerndigital.com/content/dam/doc-library/en_us/assets/public/western-digital/product/data-center-drives/ultrastar-dc-hc600-series/product-manual-ultrastar-dc-hc670-sata-spec.pdf
1. "256MiB zone size (Conventional/Sequential Write required)"
6. Heat management in AWS S3
1. When disks accumulating heat, you accumulates delay. (Queuing, stalling, tail latency)
2. Balancing heat is needed. Individual workloads are bursty
1. Aggregating loads from many users
1. My questions
1. How to handle big customers that can occupy an entire cluster?
7. Data sharding and replication
1. Bucket size 3.7PB, Peak throughput 2.3M req/s. Per disk gives 120 IOPS. Disk size 26TB.
Shard data to as many disks as possible. Need 19K disks to provide that level of throughput
1. Good point. Scale allows AWS S3 to deliver performance for customers that would otherwise be prohibitive to build
1. I.e. the customer cannot just buy 19K HDDs in its own datacenter
2. Another point is, customer doesn't need to provision hardware for peak throughput.
Cloud aggregates workloads to amortize cost.
2. Sharding data strips should be needed.
8. In video 33:00 about ShardStore
1. ShardStore: Using Lightweight Formal Methods to Validate a Key-Value Storage Node in Amazon S3
https://www.cs.utexas.edu/~bornholt/papers/shardstore-sosp21.pdf
2. ShardStore rewrites the bottle layer of AWS S3, to work with zoned devices (should be SMR/ZNS drives) and their IO constraints
3. ShardStore is running Rust.
3. ShardStore is using Soft Updates.
1. To avoid the cost of redirecting writes through a write-ahead log
2. And to allow flexibility in physical placement of data on disk
3. My questions
1. Can Soft Update be implemented equivalently with Group Flush / Group Commit?
9. Durability mechanisms
1. Durability reviews - an idea from Threat Model in security area
2. ShardStore: Lightweight Formal Verification
3. Rollout new version on a shard by shard basis
4. Help customers design for durability
1. accidentally delete data is a big issue
2. bug in code that accidentally delete/corrupt data
3. privacy regulations, GDPR
4. object versioning, object lock
5. cross region replication (CRR) that switched account
60. 技术管理:绩效辅导 - 赵俊民的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/664104692
1. Very good. Such materials are rarely shared. They can be used as a reference to learn management.
61. LLM safety文章一览:如何构建更安全的language model - yearn的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/664096097
1. "红队测试被认为是一个潜在有效的工具,可用于对语言模型的有害输出进行对抗性检测,然后更新模型以避免这些输"
63. 漫谈高性能计算与性能优化:访存 - 有了琦琦的棍子的文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/600489819
0. very good summary, in-depth thinking, and useful referenced docs
1. GPU、内存。IO可以被看作"存储"。计算机优化可以被归结为访存优化。
1. 访存优化这个第一性原理
1. memory wall
2. 三板斧:一是减少数据搬运,二是减少数据访存延时,三是保证负载均衡
n. related materials
1. AI算力的阿喀琉斯之踵:内存墙 - OneFlow
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/363041668
1. interesting summary. very useful growth projections
2. 稀疏矩阵存储格式总结+存储效率对比:COO,CSR,DIA,ELL,HYB
https://www.cnblogs.com/xbinworld/p/4273506.html
67. SRE Best Practices for Capacity Management - Luis Quesada Torres and Doug Colish @ Google
https://static.googleusercontent.com/media/sre.google/en//static/pdf/login_winter20_10_torres.pdf
1. Practical summary for concepts, factors, and practices in resource provisioning and capacity planning. Good.
2. highlights
1. The goal of capacity management is controlling uncertainty
1. Peak Usage, Maximum Peak Utilization, Redundancy (and region)
2. extra load due to redundancy
3. latency-sensitive and latency-insensitive loads
4. Spare capacity - Additional Resources for the Unknown
2. Capacity Planning
1. While resource provisioning refers to the process of determining the correct amount of resources to keep your service running right now, capacity planning entails forecasting demand to guarantee resource supply in the future.
1. for example, your resource needs in three months, six months, or a year
2. capacity planning uses historic demand to forecast growth to build on top of resource provisioning for your service's maximum peak utilization, redundancy requirements, latency-insensitive processes, and the unknown factor.
1. Generally, you'll want to add to this forecast any planned new consumers of your resources, including new services, marketing campaigns, new features, etc.
2. (# of different components) × (# of instances of each component) × (# of regions) × (# of datapoints) × (other contributing factors)
3. Service demand
1. Other unexpected events like natural disasters, network interrupts, or power outages can drastically alter your traffic patterns
2. Even planned situations such as social events or the beginning or end of holidays can affect your service in unexpected ways
3. Best practices
1. Load Testing
1. Run a small replica of the service at target utilization and above, and exercise failover, cache failures, rollouts, etc
2. Holistically Evaluate the Capacity
1. A regression test and evaluation of the prediction quality
3. Decrease the Impact of Outages
1. Graceful degradation.
2. Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack protection.
3. Effective timeouts.
4. Load shedding.
4. Quota Management and Throttling
5. Monitoring and Alerting
1. Load metrics
2. Resource metrics
3. Performance metrics
4. High-level health metrics
6. Resource Pooling
1. several services share resources
7. General SRE Best Practices
1. store the capacity state as a configuration in a version control system and require peer reviews for any changes
2. Automate enforcement, roll out all changes gradually, constantly monitor your service, and be ready to roll back if needed
3. In the event of a failure or other issue, exercise blameless postmortems to honestly learn from the mistakes, and commit to improving the system to avoid repeating them.
4. Evaluating a Service for Capacity
1. When evaluating capacity for a new or existing service, we recommend determining its resource requirements by following these steps:
1. Estimate the resources needed to serve the expected load.
1. Use the template in Table 1 and fill it in with the expected service demand for the different resource classes.
2. Table below
Hardware Specs
Processors CPU type and count (cores)
Graphics Processing Units GPU type and count
Storage HDD (hard drives) and SSD (solid state disk):
• Amount of storage (TB)
• Bandwidth
• IOPS
Network Intra datacenter, inter datacenter, ISP access:
• Latencies
• Bandwidth
Back Ends Services and capacity needed
Other AI accelerators, other special hardware
2. Calculate and factor in the target utilization of the different components of the service. You may need to perform load testing to assess:
1. Peak usage
2. Maximum peak utilization
3. Redundancy
4. Latency-insensitive processes
5. Spare resources for the unknowns
3. Consider aspects such as:
1. Priority
2. Region
3. Service components
4. Specific points in time and time into the future (monthly, quarterly, for six months, a year, etc.)
4. Perform forecasting, considering whether you need to plan for capacity per:
1. Priority
2. Region
3. Service components
4. Number of points in time per year
5. Continue to learn about capacity management:
1. Watch the video "Complexities of Capacity Management for Distributed Services" for an extended tech talk on the topic [1].
2. Read the ;login: article "Capacity Planning" [2].
3. Review the "Software Engineering in SRE," "Managing Critical State," and "Reliable Product Launches at Scale" chapters of Google's Site Reliability Engineering [3].
Create an Issue or comment below