Play with Openstack Swift
Swift is used in Openstack for
- Glance backend for image storage.
- A public object storage service open to tentants.
Architecture and Concepts
A good swift architecture doc here.
Different Services
The four Swift server processes are proxy, account, container and object.
- Proxy processes: User restful http request entry, distribute request to storage nodes. Share nothing, stateless.
- Account processes: Handle metadata for accounts: account info and list containers in a account. Stored as sqlite on disk.
- Container processes: Handle metadata for containers: list objects. Stored as sqllite on disk.
- Object processes: Store object data.
- Auditors: run on storage node, scan & repair bit-rot.
- Replicators: maintain object copies. Only push to other nodes.
Swift container is the corresponding concept to AWS S3 bucket and Ceph pool. It is a group, where you put objects and apply config.
Storage structure can be seen as /account/container/object.
Zones and Regions
Swift cluster concepts below.
- Nodes: a machine.
- Zones: also called avaibility zones. One zone corresponds (usually) a rack in a datacenter.
- Regions: (usually) refer to different datacenters in different geographical sites.
There can have other layouts for region and zone but above is easier. Region and zone seperate failure domains. AWS has same concept. Ceph use CRUSH map to address them.
A cluster that is using two or more regions is a multi-region cluster. Also note that swift is eventual consistency.
Object Distribution
Dynamo has virtual node, swift has partition, while Ceph has PG. Mapping workflow is: object key -> which virtual node/partition/PG to put object -> which device contains virtual node/partition/PG. Virtual node/partition/PG are the smallest unit to operate on, rather than objects. Replication, recovery, consistency checking operate on the layer of virtual node/partitoin/PG.
A virtual node/partitoin/PG‘s size and their total count can not be changed. Which object maps to which virtual node/partitoin/PG (usually a simple mod %) can not be changed. What can changed which virtual node/partitoin/PG put on which node/drive.
For this step, Dynamo use consistent hashing, Swift use ring file lookup, while Cepu use CRUSH map. Swift ring file is pure static and lookup destination node/drive. Ceph CRUSH map is pure computational which computes destination node/drive.
This can be seen as dimensional reduction, since if we directly operate on objects, there will be too many of them and metadata explodes.
For Swift, a partition is just a directory sitting on a disk with a corresponding hash table of what it contains. For Ceph, a PG is just a string prefix in keys in leveldb (the leveldb backend mode), a logical separator.
Ring File
Refer to here. Ring file contains 2 tables:
1 - Devices lookup table
Row key is replica copies. Column key is partition id. Cell contains device id. A device is a disk drive where partition is stored.
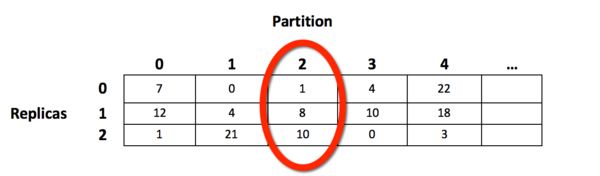
2 - The devices list
Colume key is device id. Cell contains device detail. Note that regions is in ring file.
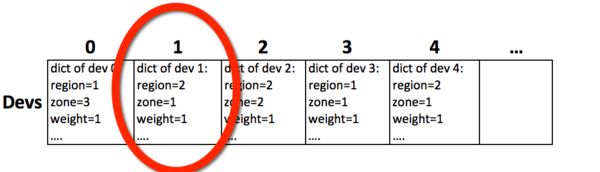
The lookup workflow is to first find device id in Devices lookup table, than find device detail in Devices lookup table. After that the process can call on correct drives.
Deployment Layout
How many partitions? Maximum number of drives the cluster will contain (in future), multiply by 100, then round up to the nearest power of two.
Proxy services are more CPU & network intensive. If you are terminating SSL traffic at proxy, greater CPU power will be required. The object, container, and account services are more disk & network intensive. Refer to guide.
One deployment layout example is:
- Proxy services alone on one node:
- swift-proxy-server, swift-object-expirer, swiftstats-server.
- memcached
- Object services, container services, account services on anther node:
- swift-object-server, swift-container-server, swift-account-server,
- swift-object-updater, swift-container-updater,
- swift-object-auditor, swift-container-auditor, swift-account-auditor,
- swift-object-replicator, swift-container-replicator, swift-account-replicator,
- swift-account-reaper, swift-container-sync, rsync
Another example is:
- Put proxy and storage all in one node.
- When add machines in, both proxy and storage horizontally grows.
The official doc example is:
- One proxy node in the front.
- A set of storage nodes.
The swift-objet-expirer can be anywhere. The rsync is used to replicate objects and whole db file in swift. Rsync runs on storage nodes.
The memcached is used for caching certain types of lookups, such as auth tokens, and container/account existence. Swift does not do any caching of actual object data. It needs RAM & CPU. Rackspace runs memcached on proxy server. The proxy-server.conf should contain all memcached servers:
memcache_servers = 10.224.155.xx1:11211,10.224.155.xx2:11211.
The disks should be local JBOD. Network structure refer to here.
Multi-region Deployment
For multi-region deployment. Usually two replicas in a single Region (the ‘primary’ location) and one replica in another Region (the ‘offsite’ location).
Multi-region in Old Times
Before Swift 1.9.0 release (2013-10-17), people craft their own ways for multi-region.
-
Container sync, capable of either 1-way or 2-way synchronization using a shared secret key. Also see here. This is the simplest way but results in 6 replicas in 2 cluster.
-
Swiftstack proposed and implements Tiered Zones, which controls replica to zones more flexibly, to overcome container sync’s problem.
-
Mirantis also proposed a solution. But it is just a proposal not implementation.
Multi-region Now
It is called global cluster now, first released in Swift 1.9.0. Global cluster should consider replica count, replica location, proxy read/write affinity, and secure link between datacenters (e.g. VPN). A thinking is that container sync is still an option even now because of the simplicity.
Current implementation of global cluster summarizes as follows:
- Add region tier above zones.
- Add read/wrtie affinity. proxy node is region awareness.
- Separated data and replication network.
- Refactored replicator. There is foreign replicator and local replicator.
Regions should be connected via VPN. Note the inconsistency window of foreign replicators, which replicates between regions, is much larger than local replicators, which replicates in one region. All regions share the same ring file, but proxy nodes in different region has different read/write affinity to region/zone.
There is no much doc found. Some references: [1][2][3][4].
Install and Configuration
Following guide saio and offical. Also this non-official one. The Deployment Guide provides various consideration and server configuration.
Environment
I want to install swift on 3 VM nodes 10.224.147.166, 10.224.147.167, 10.224.147.168 of CentOS 7. Each contains both proxy and storage services. The storage disks will use loop device to “fake”. Install from source.
All CentOS 7 nodes has passed through the “CentOS 7 Preparation” step, one of my prior blog post.
Prerequisites
First to install dependencies. On each node, install below packages. Acutally I use ansible to batch command.
yum install -y curl gcc memcached rsync sqlite xfsprogs git-core libffi-devel xinetd python-setuptools python-coverage python-devel python-nose python-simplejson pyxattr python-eventlet python-greenlet python-paste-deploy python-netifaces python-pip python-dns python-mock
Add a user for swift.
useradd -r -s /sbin/nologin swift
Next I need to prepare disks for swift. I use loop device to fake disk from a file. Run below on each node.
mkdir -p /srv/node/sdb1
dd if=/dev/zero of=/srv/swift_disk.img bs=1 count=1 seek=1G
mkfs.xfs -f -i size=1024 /srv/swift_disk.img
# to peresist mount config on restart you need /etc/fstab
mount -t xfs -o noatime,nodiratime,nobarrier,logbufs=8 /srv/swift_disk.img /srv/node/sdb1
rm -rf /srv/node/sdb1/*
chmod go-rwx /srv/node
chown -R swift:swift /srv/node
Prepare other directories.
mkdir -p /var/log/swift
chown -R swift:swift /var/log/swift
mkdir -p /var/run/swift
mkdir -p /var/cache/swift
chown -R swift:swift /var/cache/swift
chown -R swift:swift /var/run/swift
mkdir -p /etc/swift
touch /etc/swift/swift.conf
Installation
Get the code
mkdir workspace
cd workspace
git clone https://github.com/openstack/python-swiftclient.git
git clone https://github.com/openstack/swift.git
cd swift
git checkout stable/juno
cd ..
Install swift
cd python-swiftclient
pip install -r requirements.txt
python setup.py install
cd ..
cd swift
pip install -r requirements.txt
python setup.py install
cd ..
Configuration
Configuration includes rsync, memcached and swift object/container/account/proxy. Swift config doc refer to here.
Rsync for Swift
Set up rsync. Rsync config file refer to here. Tutorial refer to here. Swift rsync config refer to here.
Fisrt let’s config rsync.
echo '
uid = nobody
gid = nobody
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid
# this should really be bound to an internal storage (replication) network (use an ip on that network)
address = 0.0.0.0
use chroot = true
timeout = 300
log format = %t %a %m %f %b
[account]
max connections = 20
path = /srv/node/
read only = false
write only = false
list = yes
uid = swift
gid = swift
incoming chmod = 0644
outgoing chmod = 0644
lock file = /var/lock/account.lock
[container]
max connections = 20
path = /srv/node/
read only = false
write only = false
list = yes
uid = swift
gid = swift
incoming chmod = 0644
outgoing chmod = 0644
lock file = /var/lock/container.lock
[object]
max connections = 20
path = /srv/node/
read only = false
write only = false
list = yes
uid = swift
gid = swift
incoming chmod = 0644
outgoing chmod = 0644
lock file = /var/lock/object.lock
' > /etc/rsyncd.conf
Start rsync with xinetd.
echo '
service rsync
{
disable = no
port = 873
socket_type = stream
protocol = tcp
wait = no
user = root
group = root
groups = yes
server = /usr/bin/rsync
server_args = --daemon
}
' > /etc/xinetd.d/rsync
# to restart xinetd
service xinetd restart
To start rsyncd. This is step is just for reference. It is NOT NEEDED because xinetd already does it.
# set start on boot
#chkconfig rsyncd on
# restart service
#service rsyncd restart
To test rsync connectivity
# do it on localhost
$ echo 'hello world 123' > /srv/node/sdb1/hello.txt
# do it on another host
$ mkdir ./rsync_test/
$ rsync -rtv rsync://swift@10.224.147.166/object/sdb1/hello.txt ./rsync_test/ # or 10.224.147.167-168
receiving incremental file list
hello.txt
sent 47 bytes received 118 bytes 110.00 bytes/sec
total size is 16 speedup is 0.10
$ rsync -rtv rsync://swift@10.224.147.166/
account
container
object
Memcached for Swift
Start memcached.
service memcached start
chkconfig memcached on
The memcached itself doesn’t know its cluster peers. It is the client’s responsibility to do consistent hashing and keep track of memcached peers.
Swift Config
Do the configuration on node 10.224.147.166 only. I will copy them to other nodes later.
First, config the swift global settings.
echo '
# random unique strings that can never change (DO NOT LOSE). should remain secret and MUST NOT change
[swift-hash]
swift_hash_path_prefix = d567525c1f822093
swift_hash_path_suffix = 72103971ef596e63
# recommended set policy 0, even you dont use it
[storage-policy:0]
name = Policy-0
default = yes
' > /etc/swift/swift.conf
Config the proxy server.
echo '
[DEFAULT]
bind_port = 8080
user = swift
worker = 32
log_facility = LOG_LOCAL1
eventlet_debug = true
#conn_timeout=3
[pipeline:main]
# for monitoring you can more add informant and recon. note that I dont use keystone here
pipeline = catch_errors gatekeeper healthcheck proxy-logging cache bulk tempurl slo dlo ratelimit crossdomain tempauth staticweb container-quotas account-quotas proxy-logging proxy-server
[filter:catch_errors]
use = egg:swift#catch_errors
[filter:healthcheck]
use = egg:swift#healthcheck
[filter:proxy-logging]
use = egg:swift#proxy_logging
[filter:bulk]
use = egg:swift#bulk
[filter:ratelimit]
use = egg:swift#ratelimit
[filter:crossdomain]
use = egg:swift#crossdomain
[filter:dlo]
use = egg:swift#dlo
[filter:slo]
use = egg:swift#slo
[filter:tempurl]
use = egg:swift#tempurl
[filter:tempauth]
use = egg:swift#tempauth
user_admin_admin = admin .admin .reseller_admin
user_test_tester = testing .admin
user_test2_tester2 = testing2 .admin
user_test_tester3 = testing3
[filter:staticweb]
use = egg:swift#staticweb
[filter:account-quotas]
use = egg:swift#account_quotas
[filter:container-quotas]
use = egg:swift#container_quotas
[filter:cache]
use = egg:swift#memcache
memcache_servers = 10.224.147.166:11211,10.224.147.167:11211,10.224.147.168:11211
[filter:gatekeeper]
use = egg:swift#gatekeeper
[app:proxy-server]
use = egg:swift#proxy
allow_account_management = true
account_autocreate = true
' > /etc/swift/proxy-server.conf
The tempauth is a lightweight authentication method in Openstack able to substitute keystone. The config lines in [filter:tempauth] defines user_<account-name>_<username-under-the-account> = <password> .<role1> .<role2> ....
Config the object expirer
echo '
[DEFAULT]
# swift_dir = /etc/swift
user = swift
# You can specify default log routing here if you want:
log_name = object-expirer
log_facility = LOG_LOCAL6
log_level = INFO
[object-expirer]
interval = 300
# auto_create_account_prefix = .
[pipeline:main]
pipeline = catch_errors cache proxy-server
[app:proxy-server]
use = egg:swift#proxy
[filter:cache]
use = egg:swift#memcache
memcache_servers = 10.224.147.166:11211,10.224.147.167:11211,10.224.147.168:11211
[filter:catch_errors]
use = egg:swift#catch_errors
' > /etc/swift/object-expirer.conf
Config the account server,
echo '
[DEFAULT]
devices = /srv/node/
mount_check = false
bind_port = 6012
workers = 1
user = swift
log_facility = LOG_LOCAL2
recon_cache_path = /var/cache/swift
eventlet_debug = true
[pipeline:main]
pipeline = recon healthcheck account-server
[app:account-server]
use = egg:swift#account
[filter:recon]
use = egg:swift#recon
[filter:healthcheck]
use = egg:swift#healthcheck
[account-replicator]
concurrency = 2
[account-auditor]
[account-reaper]
' > /etc/swift/account-server.conf
Config the container server.
echo '
[DEFAULT]
devices = /srv/node
mount_check = false
disable_fallocate = true
bind_port = 6011
workers = 1
user = swift
log_facility = LOG_LOCAL2
recon_cache_path = /var/cache/swift
eventlet_debug = true
allow_versions = true
[pipeline:main]
pipeline = recon healthcheck container-server
[app:container-server]
use = egg:swift#container
[filter:recon]
use = egg:swift#recon
[filter:healthcheck]
use = egg:swift#healthcheck
[container-replicator]
concurrency = 2
[container-updater]
concurrency = 2
[container-auditor]
[container-sync]
' > /etc/swift/container-server.conf
Config the object server.
echo '
[DEFAULT]
devices = /srv/node
mount_check = false
bind_port = 6010
workers = 1
user = swift
log_facility = LOG_LOCAL2
recon_cache_path = /var/cache/swift
eventlet_debug = true
[pipeline:main]
pipeline = recon healthcheck object-server
[app:object-server]
use = egg:swift#object
[filter:recon]
use = egg:swift#recon
[filter:healthcheck]
use = egg:swift#healthcheck
[object-replicator]
concurrency = 2
[object-updater]
concurrency = 2
[object-auditor]
' > /etc/swift/object-server.conf
Set the permissioins
chown -R swift:swift /etc/swift
chmod 640 /etc/swift/swift.conf
At last, you should maintain the config files synchronized (except ip addresses) across Swift cluster. You can see from above config files that, Swift services know nothing about their peers. Only the ring file knows cluster layout.
Swift Ring File
Do the configuration on 10.224.147.166 only. I will copy them to other nodes later.
First, to remove existing ring file
cd /etc/swift
rm -f *.builder *.ring.gz backups/*.builder backups/*.ring.gz
Following the guide, section “Create initial rings”. Also swift-ring-builder manual here.
Create the ring file.
swift-ring-builder object.builder create 9 3 1
swift-ring-builder object.builder add r1z1-10.224.147.166:6010/sdb1 1
swift-ring-builder object.builder add r1z2-10.224.147.167:6010/sdb1 1
swift-ring-builder object.builder add r1z3-10.224.147.168:6010/sdb1 1
swift-ring-builder container.builder create 9 3 1
swift-ring-builder container.builder add r1z1-10.224.147.166:6011/sdb1 1
swift-ring-builder container.builder add r1z2-10.224.147.167:6011/sdb1 1
swift-ring-builder container.builder add r1z3-10.224.147.168:6011/sdb1 1
swift-ring-builder account.builder create 9 3 1
swift-ring-builder account.builder add r1z1-10.224.147.166:6012/sdb1 1
swift-ring-builder account.builder add r1z2-10.224.147.167:6012/sdb1 1
swift-ring-builder account.builder add r1z3-10.224.147.168:6012/sdb1 1
swift-ring-builder object.builder rebalance
swift-ring-builder container.builder rebalance
swift-ring-builder account.builder rebalance
Note that the object.builder, container.builder, account.builder here are file names actually. The ip addresses here should be “STORAGE_NODE_MANAGEMENT_INTERFACE_IP_ADDRESS”, according to section “Create initial rings”.
To list devices in ring file
$ swift-ring-builder account.builder
account.builder, build version 3
512 partitions, 3.000000 replicas, 1 regions, 3 zones, 3 devices, 0.00 balance
The minimum number of hours before a partition can be reassigned is 1
Devices: id region zone ip address port replication ip replication port name weight partitions balance meta
0 1 1 10.224.147.166 6012 10.224.147.166 6012 sdb1 1.00 512 0.00
1 1 2 10.224.147.167 6012 10.224.147.167 6012 sdb1 1.00 512 0.00
2 1 3 10.224.147.168 6012 10.224.147.168 6012 sdb1 1.00 512 0.00
$ swift-ring-builder object.builder
object.builder, build version 3
512 partitions, 3.000000 replicas, 1 regions, 3 zones, 3 devices, 0.00 balance
The minimum number of hours before a partition can be reassigned is 1
Devices: id region zone ip address port replication ip replication port name weight partitions balance meta
0 1 1 10.224.147.166 6010 10.224.147.166 6010 sdb1 1.00 512 0.00
1 1 2 10.224.147.167 6010 10.224.147.167 6010 sdb1 1.00 512 0.00
2 1 3 10.224.147.168 6010 10.224.147.168 6010 sdb1 1.00 512 0.00
$ swift-ring-builder container.builder
container.builder, build version 3
512 partitions, 3.000000 replicas, 1 regions, 3 zones, 3 devices, 0.00 balance
The minimum number of hours before a partition can be reassigned is 1
Devices: id region zone ip address port replication ip replication port name weight partitions balance meta
0 1 1 10.224.147.166 6011 10.224.147.166 6011 sdb1 1.00 512 0.00
1 1 2 10.224.147.167 6011 10.224.147.167 6011 sdb1 1.00 512 0.00
2 1 3 10.224.147.168 6011 10.224.147.168 6011 sdb1 1.00 512 0.00
$ swift-ring-builder object.builder search d1
Devices: id region zone ip address port replication ip replication port name weight partitions balance meta
1 1 2 10.224.147.167 6010 10.224.147.167 6010 sdb1 1.00 512 0.00
$ swift-ring-builder object.builder search d0
Devices: id region zone ip address port replication ip replication port name weight partitions balance meta
0 1 1 10.224.147.166 6010 10.224.147.166 6010 sdb1 1.00 512 0.00
To see partition device mapping in ring file, refering to here. I don’t find proper tools.
python
>>> from swift.common.ring import RingData, RingBuilder
>>> ring = RingData.load('/etc/swift/account.ring.gz')
>>> ring._replica2part2dev_id
To see which objects on a which node. (But the name is hashed).
ls -l /srv/node/sdb/objects/
Distribute ring file to all nodes. Here I also copy config files.
# execute on host 10.224.147.166
scp -r /etc/swift/* root@10.224.147.167:/etc/swift/
scp -r /etc/swift/* root@10.224.147.168:/etc/swift/
# on host 10.224.147.167
chown -R swift:swift /etc/swift
chmod 640 /etc/swift/swift.conf
# on host 10.224.147.168
chown -R swift:swift /etc/swift
chmod 640 /etc/swift/swift.conf
Swift Startup
Use swift-init to manage swift services. On each node execute
# start proxy, account, container, object services
swift-init main start
# start updater, replicator, auditor, reaper, etc. all background daemons
swift-init rest start
Ignore container-reconciler, I dont’t use it here.
To see log
less /var/log/messages
After all nodes are started up, see processes
$ ps -ef|grep swift
swift 20764 1 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-container-updater /etc/swift/container-server.conf
swift 20765 1 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-account-auditor /etc/swift/account-server.conf
swift 20766 1 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-object-replicator /etc/swift/object-server.conf
swift 20767 1 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-container-sync /etc/swift/container-server.conf
swift 20768 1 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-container-replicator /etc/swift/container-server.conf
swift 20769 1 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-object-auditor /etc/swift/object-server.conf
swift 20770 1 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-object-expirer /etc/swift/object-expirer.conf
swift 20771 1 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-container-auditor /etc/swift/container-server.conf
swift 20772 1 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-container-server /etc/swift/container-server.conf
swift 20773 1 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-object-server /etc/swift/object-server.conf
swift 20775 1 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-account-reaper /etc/swift/account-server.conf
swift 20778 1 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-proxy-server /etc/swift/proxy-server.conf
swift 20781 1 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-account-replicator /etc/swift/account-server.conf
swift 20785 1 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-object-updater /etc/swift/object-server.conf
swift 20790 1 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-account-server /etc/swift/account-server.conf
swift 20879 20773 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-object-server /etc/swift/object-server.conf
swift 20884 20772 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-container-server /etc/swift/container-server.conf
swift 20888 20790 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-account-server /etc/swift/account-server.conf
swift 20892 20778 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-proxy-server /etc/swift/proxy-server.conf
swift 20893 20778 0 12:57 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/swift-proxy-server /etc/swift/proxy-server.conf
root 20983 4434 0 12:57 pts/1 00:00:00 grep --color=auto swift
Verify Operation
Verify the installation functioning, refer to here the “Verify operation” section. For swift client guide, see here and here. Verify operation
# execute on 10.224.147.166
cd ~
# show swift status
swift -A http://10.224.147.168:8080/auth/v1.0 -U admin:admin -K admin stat
# create random object file
dd if=/dev/urandom of=./obj1.dat bs=512 count=2048
dd if=/dev/urandom of=./obj2.dat bs=512 count=2048
# update objects from different proxy
swift -A http://10.224.147.168:8080/auth/v1.0 -U admin:admin -K admin upload container1 obj1.dat
swift -A http://10.224.147.167:8080/auth/v1.0 -U admin:admin -K admin upload container1 obj2.dat
swift -A http://10.224.147.168:8080/auth/v1.0 -U admin:admin -K admin upload container2 obj1.dat
Do some verification.
# # execute on 10.224.147.168, we should see 2 containers
$ swift -A http://10.224.147.167:8080/auth/v1.0 -U admin:admin -K admin list
container1
container2
$ swift -A http://10.224.147.166:8080/auth/v1.0 -U admin:admin -K admin list
container1
container2
$ swift -A http://10.224.147.166:8080/auth/v1.0 -U admin:admin -K admin stat
Account: AUTH_admin
Containers: 2
Objects: 3
Bytes: 3145728
Containers in policy "policy-0": 2
Objects in policy "policy-0": 3
Bytes in policy "policy-0": 3145728
Connection: keep-alive
X-Timestamp: 1415699934.50787
X-Trans-Id: tx28cbfe71ffd846d99770e-005461e275
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
Accept-Ranges: bytes
On host 10.224.147.166, list storage files. I want to keep the file layout printed for future reference.
$ ls -lR /srv/node
/srv/node:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 6 swift swift 78 Nov 11 09:58 sdb1
/srv/node/sdb1:
total 4
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 16 Nov 11 09:58 accounts
drwxr-xr-x 4 swift swift 26 Nov 11 09:59 containers
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 16 Nov 11 04:55 hello.txt
drwxr-xr-x 5 swift swift 35 Nov 11 09:59 objects
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 6 Nov 11 09:59 tmp
/srv/node/sdb1/accounts:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 16 Nov 11 09:58 122
/srv/node/sdb1/accounts/122:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:58 d44
/srv/node/sdb1/accounts/122/d44:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 110 Nov 11 10:02 3d7488d535e52f75dd1f0bd1c225fd44
/srv/node/sdb1/accounts/122/d44/3d7488d535e52f75dd1f0bd1c225fd44:
total 20
-rw------- 1 swift swift 17408 Nov 11 10:02 3d7488d535e52f75dd1f0bd1c225fd44.db
-rw-r--r-- 1 swift swift 0 Nov 11 10:02 3d7488d535e52f75dd1f0bd1c225fd44.db.pending
/srv/node/sdb1/containers:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 16 Nov 11 09:58 248
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 16 Nov 11 09:59 388
/srv/node/sdb1/containers/248:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:58 ca5
/srv/node/sdb1/containers/248/ca5:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 110 Nov 11 10:00 7c4849d705bebcde302084f4c1eb6ca5
/srv/node/sdb1/containers/248/ca5/7c4849d705bebcde302084f4c1eb6ca5:
total 20
-rw------- 1 swift swift 18432 Nov 11 10:00 7c4849d705bebcde302084f4c1eb6ca5.db
-rw-r--r-- 1 swift swift 0 Nov 11 09:59 7c4849d705bebcde302084f4c1eb6ca5.db.pending
/srv/node/sdb1/containers/388:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:59 36e
/srv/node/sdb1/containers/388/36e:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 110 Nov 11 10:00 c236994db779c389722290de9cfe736e
/srv/node/sdb1/containers/388/36e/c236994db779c389722290de9cfe736e:
total 20
-rw------- 1 swift swift 18432 Nov 11 10:00 c236994db779c389722290de9cfe736e.db
-rw-r--r-- 1 swift swift 0 Nov 11 09:59 c236994db779c389722290de9cfe736e.db.pending
/srv/node/sdb1/objects:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:59 143
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:59 34
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:58 374
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/143:
total 4
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:59 f5f
-rw------- 1 swift swift 48 Nov 11 09:59 hashes.pkl
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/143/f5f:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 34 Nov 11 09:59 47ecc178bfb17067f56719b09038ff5f
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/143/f5f/47ecc178bfb17067f56719b09038ff5f:
total 1024
-rw------- 1 swift swift 1048576 Nov 11 09:59 1415699951.85503.data
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/34:
total 4
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:59 1b9
-rw------- 1 swift swift 48 Nov 11 09:59 hashes.pkl
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/34/1b9:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 34 Nov 11 09:59 112c5d2b28d0bf61d12ef3885045c1b9
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/34/1b9/112c5d2b28d0bf61d12ef3885045c1b9:
total 1024
-rw------- 1 swift swift 1048576 Nov 11 09:59 1415699969.37921.data
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/374:
total 4
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:58 0e8
-rw------- 1 swift swift 48 Nov 11 09:58 hashes.pkl
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/374/0e8:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 34 Nov 11 09:58 bb45bcc3fe35df8e2218c77fb48d30e8
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/374/0e8/bb45bcc3fe35df8e2218c77fb48d30e8:
total 1024
-rw------- 1 swift swift 1048576 Nov 11 09:58 1415699934.75348.data
/srv/node/sdb1/tmp:
total 0
On host 10.224.147.167, list storage files.
$ ls -lR /srv/node
/srv/node:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 6 swift swift 78 Nov 11 09:58 sdb1
/srv/node/sdb1:
total 4
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 16 Nov 11 09:58 accounts
drwxr-xr-x 4 swift swift 26 Nov 11 09:59 containers
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 16 Nov 11 09:29 hello.txt
drwxr-xr-x 5 swift swift 35 Nov 11 09:59 objects
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 6 Nov 11 09:59 tmp
/srv/node/sdb1/accounts:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 16 Nov 11 09:58 122
/srv/node/sdb1/accounts/122:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:58 d44
/srv/node/sdb1/accounts/122/d44:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 110 Nov 11 10:03 3d7488d535e52f75dd1f0bd1c225fd44
/srv/node/sdb1/accounts/122/d44/3d7488d535e52f75dd1f0bd1c225fd44:
total 20
-rw------- 1 swift swift 17408 Nov 11 10:03 3d7488d535e52f75dd1f0bd1c225fd44.db
-rw-r--r-- 1 swift swift 0 Nov 11 10:02 3d7488d535e52f75dd1f0bd1c225fd44.db.pending
/srv/node/sdb1/containers:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 16 Nov 11 09:58 248
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 16 Nov 11 09:59 388
/srv/node/sdb1/containers/248:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:58 ca5
/srv/node/sdb1/containers/248/ca5:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 110 Nov 11 10:02 7c4849d705bebcde302084f4c1eb6ca5
/srv/node/sdb1/containers/248/ca5/7c4849d705bebcde302084f4c1eb6ca5:
total 20
-rw------- 1 swift swift 18432 Nov 11 10:02 7c4849d705bebcde302084f4c1eb6ca5.db
-rw-r--r-- 1 swift swift 0 Nov 11 09:59 7c4849d705bebcde302084f4c1eb6ca5.db.pending
/srv/node/sdb1/containers/388:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:59 36e
/srv/node/sdb1/containers/388/36e:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 110 Nov 11 10:02 c236994db779c389722290de9cfe736e
/srv/node/sdb1/containers/388/36e/c236994db779c389722290de9cfe736e:
total 20
-rw------- 1 swift swift 18432 Nov 11 10:02 c236994db779c389722290de9cfe736e.db
-rw-r--r-- 1 swift swift 0 Nov 11 09:59 c236994db779c389722290de9cfe736e.db.pending
/srv/node/sdb1/objects:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:59 143
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:59 34
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:58 374
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/143:
total 4
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:59 f5f
-rw------- 1 swift swift 48 Nov 11 09:59 hashes.pkl
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/143/f5f:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 34 Nov 11 09:59 47ecc178bfb17067f56719b09038ff5f
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/143/f5f/47ecc178bfb17067f56719b09038ff5f:
total 1024
-rw------- 1 swift swift 1048576 Nov 11 09:59 1415699951.85503.data
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/34:
total 4
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:59 1b9
-rw------- 1 swift swift 48 Nov 11 09:59 hashes.pkl
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/34/1b9:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 34 Nov 11 09:59 112c5d2b28d0bf61d12ef3885045c1b9
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/34/1b9/112c5d2b28d0bf61d12ef3885045c1b9:
total 1024
-rw------- 1 swift swift 1048576 Nov 11 09:59 1415699969.37921.data
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/374:
total 4
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:58 0e8
-rw------- 1 swift swift 48 Nov 11 09:58 hashes.pkl
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/374/0e8:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 34 Nov 11 09:58 bb45bcc3fe35df8e2218c77fb48d30e8
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/374/0e8/bb45bcc3fe35df8e2218c77fb48d30e8:
total 1024
-rw------- 1 swift swift 1048576 Nov 11 09:58 1415699934.75348.data
/srv/node/sdb1/tmp:
total 0
On host 10.224.147.168, list storage files.
$ ls -lR /srv/node
/srv/node:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 6 swift swift 62 Nov 11 09:58 sdb1
/srv/node/sdb1:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 16 Nov 11 09:58 accounts
drwxr-xr-x 4 swift swift 26 Nov 11 09:59 containers
drwxr-xr-x 5 swift swift 35 Nov 11 09:59 objects
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 6 Nov 11 09:59 tmp
/srv/node/sdb1/accounts:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 16 Nov 11 09:58 122
/srv/node/sdb1/accounts/122:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:58 d44
/srv/node/sdb1/accounts/122/d44:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 110 Nov 11 10:03 3d7488d535e52f75dd1f0bd1c225fd44
/srv/node/sdb1/accounts/122/d44/3d7488d535e52f75dd1f0bd1c225fd44:
total 20
-rw------- 1 swift swift 17408 Nov 11 10:03 3d7488d535e52f75dd1f0bd1c225fd44.db
-rw-r--r-- 1 swift swift 0 Nov 11 10:02 3d7488d535e52f75dd1f0bd1c225fd44.db.pending
/srv/node/sdb1/containers:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 16 Nov 11 09:58 248
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 16 Nov 11 09:59 388
/srv/node/sdb1/containers/248:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:58 ca5
/srv/node/sdb1/containers/248/ca5:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 110 Nov 11 10:01 7c4849d705bebcde302084f4c1eb6ca5
/srv/node/sdb1/containers/248/ca5/7c4849d705bebcde302084f4c1eb6ca5:
total 20
-rw------- 1 swift swift 18432 Nov 11 10:01 7c4849d705bebcde302084f4c1eb6ca5.db
-rw-r--r-- 1 swift swift 0 Nov 11 09:59 7c4849d705bebcde302084f4c1eb6ca5.db.pending
/srv/node/sdb1/containers/388:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:59 36e
/srv/node/sdb1/containers/388/36e:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 110 Nov 11 10:01 c236994db779c389722290de9cfe736e
/srv/node/sdb1/containers/388/36e/c236994db779c389722290de9cfe736e:
total 20
-rw------- 1 swift swift 18432 Nov 11 10:01 c236994db779c389722290de9cfe736e.db
-rw-r--r-- 1 swift swift 0 Nov 11 09:59 c236994db779c389722290de9cfe736e.db.pending
/srv/node/sdb1/objects:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:59 143
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:59 34
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:58 374
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/143:
total 4
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:59 f5f
-rw------- 1 swift swift 48 Nov 11 09:59 hashes.pkl
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/143/f5f:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 34 Nov 11 09:59 47ecc178bfb17067f56719b09038ff5f
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/143/f5f/47ecc178bfb17067f56719b09038ff5f:
total 1024
-rw------- 1 swift swift 1048576 Nov 11 09:59 1415699951.85503.data
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/34:
total 4
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:59 1b9
-rw------- 1 swift swift 48 Nov 11 09:59 hashes.pkl
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/34/1b9:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 34 Nov 11 09:59 112c5d2b28d0bf61d12ef3885045c1b9
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/34/1b9/112c5d2b28d0bf61d12ef3885045c1b9:
total 1024
-rw------- 1 swift swift 1048576 Nov 11 09:59 1415699969.37921.data
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/374:
total 4
drwxr-xr-x 3 swift swift 45 Nov 11 09:58 0e8
-rw------- 1 swift swift 48 Nov 11 09:58 hashes.pkl
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/374/0e8:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 swift swift 34 Nov 11 09:58 bb45bcc3fe35df8e2218c77fb48d30e8
/srv/node/sdb1/objects/374/0e8/bb45bcc3fe35df8e2218c77fb48d30e8:
total 1024
-rw------- 1 swift swift 1048576 Nov 11 09:58 1415699934.75348.data
/srv/node/sdb1/tmp:
total 0
Download objects
# execute on 10.224.147.167
cd ~
swift -A http://10.224.147.166:8080/auth/v1.0 -U admin:admin -K admin download container1 obj2.dat
swift -A http://10.224.147.168:8080/auth/v1.0 -U admin:admin -K admin download container2 obj1.dat
To verify downloaded objects, by comparing md5
# execute on 10.224.147.167
$ echo obj1.dat | md5sum
072964ee04eb1f26cd5e6496d862fdb2 -
$ echo obj2.dat | md5sum
b194d835311f2868ce4065b00def6204 -
# execute on 10.224.147.166
$ echo obj1.dat | md5sum
072964ee04eb1f26cd5e6496d862fdb2 -
$ echo obj2.dat | md5sum
b194d835311f2868ce4065b00def6204 -
Monitoring
For monitoring you can use swift recon, statD + informant, or monitd, see here.
Create an Issue or comment below